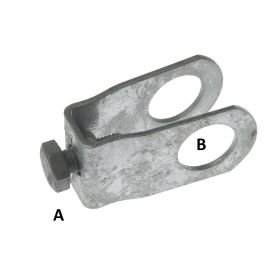
Preventing Misalignment and Instability in Pipe Structures with Cross Connectors
A poorly secured pipe framework weakens over time, leading to misalignment, instability, and
structural failure. External forces such as wind loads, movement, and uneven weight distribution put
stress on connection points, causing loosened fittings, increased wear, and potential safety risks. A
cross connector strengthens pipe connections by locking intersecting pipes firmly in place, maintaining
alignment, even weight distribution, and long-term stability without the need for welding.
Cross Connectors Used in Stable Roofing, Fencing, Feeding Barriers, and Enclosures
In stable construction, cross connectors are
essential for feeding barriers, fencing systems, and roof
supports. These fittings link horizontal and vertical pipes, forming rigid, load-bearing frameworks
capable of handling livestock movement and external pressure.
Feeding barriers must withstand constant force while remaining adaptable for layout adjustments or
expansions. Secure pipe joints in fencing systems prevent panel shifting and structural weakness,
which is especially important in high-traffic enclosures. For stable roofing, cross connectors anchor
support beams and framework elements, ensuring resistance to wind loads, temperature shifts, and
roofing weight.
The ability to assemble, modify, or expand these structures efficiently makes cross connectors a
practical and durable solution for agricultural enclosures.
Cross Connectors Used in Greenhouse Roofing, Support Beams, and Frameworks
In greenhouse construction, cross
connectors create rigid support structures for glazing panels,
ventilation systems, and irrigation lines. By securing horizontal and vertical beams, frame stability is
maintained against wind pressure, fluctuating temperatures, and seasonal stress factors.
A properly reinforced framework is crucial for sidewalls and roofing, where temperature variations can
cause expansion and contraction. Secure pipe connections prevent frame distortion, ensuring that
insulation, airflow, and protective coverings remain intact.
Cross connectors also allow for modular greenhouse expansion, making it possible to modify
assemblies without dismantling the framework. This flexibility is essential for crop rotations,
ventilation improvements, and seasonal adjustments.
Choosing the Right Coating for Long-Term Protection
Selecting the correct material coating ensures that cross connectors remain resistant to corrosion,
mechanical stress, and environmental exposure. Each galvanisation process provides a different level
of protection, depending on the application.
Hot-Dip Galvanisation
A hot-dip
galvanised coating forms a thick zinc layer that bonds to the metal surface, offering superior
protection against rust and environmental damage. This extended durability makes it ideal for
greenhouses, livestock enclosures, and storage facilities, where humidity and corrosive elements
accelerate material degradation.
Electro-Galvanisation
An electro-galvanised
coating consists of a thin, uniform zinc layer, offering moderate corrosion
resistance while maintaining a smooth surface. This type of coating works well for warehouse storage
racks, modular shelving, and transport enclosures, where exposure to heavy moisture remains
minimal.
Thermal Galvanisation
A thermally galvanised coating reinforces the surface, allowing the material to withstand mechanical
stress, repeated adjustments, and exposure to harsh conditions. Its corrosion-resistant properties
make it the preferred choice for greenhouses, livestock enclosures, and storage facilities, where
humidity and chemical exposure threaten the stability of the framework.
Applying the correct protective coating ensures that cross connectors maintain structural integrity,
resist corrosion, and extend the lifespan of modular and industrial pipe assemblies. Selecting the right
material guarantees reliable performance in demanding applications.
Correct Placement of Cross Connectors
Cross connectors play a crucial role in reinforcing pipe structures, preventing frame
distortion,
misalignment, and weak joints. Proper placement ensures that frameworks remain stable under
continuous load and external pressure.
A corner connection provides additional rigidity and prevents twisting or lateral movement within the
frame. Without reinforcement, wind loads and impact forces can cause joints to shift, weakening load-
bearing stability over time. A securely positioned cross connector prevents these issues, distributing
load forces evenly across the framework.
A midpoint connection prevents long pipe sections from bending or experiencing uneven weight
distribution. Without reinforcement, gravity and mechanical stress may cause pipes to sag, reducing
the framework’s load-bearing capacity. Anchoring pipes at the right points helps distribute weight
evenly and minimises unnecessary strain.
At high-load intersections, additional reinforcement is required to absorb stress from repeated
movement and heavy pressure. If these critical points lack support, constant strain can lead to material
fatigue and structural misalignment. A well-placed cross connector helps distribute forces evenly,
extending the durability of the entire structure.
Securing Cross Connectors
To achieve a rigid and load-bearing cross connection, installation requires precise alignment, uniform
fastening, and verified load distribution. Each step in this process ensures that pipe assemblies remain
structurally stable, resistant to movement, and capable of supporting continuous mechanical stress
and heavy loads.
Aligning the Pipes Correctly
Before installing the cross connector, ensure that pipes are positioned precisely at the correct
intersection point and angle. The surfaces must be clean and free of dust, rust, grease, or debris, as
contaminants reduce grip strength and may lead to joint instability under load.
Positioning the Cross Connector
Place the cross connector over the joint, ensuring that both pipes fit securely within the clamping
section without force. If the connector allows for adjustments, ensure proper positioning before
fastening to prevent misalignment that could compromise the overall framework under stress.
Tightening the Fasteners Evenly
Fasten bolts or screws gradually in a cross-pattern, applying equal pressure to both sides. Over-
tightening may deform the pipe or connector, while under-tightening reduces load stability. Using a
torque wrench ensures that fastening force matches manufacturer specifications, creating a secure,
evenly distributed joint.
Checking Stability and Alignment
Once secured, apply manual force or simulated load pressure to the pipes to check for any shifting or
movement. If instability occurs, re-tighten the fasteners to eliminate play. The connector should sit
flush against both pipes, ensuring even weight distribution and no stress points.
Performing a Final Load Test
For load-bearing supports, apply a test load that reflects expected weight distribution and operational
forces. In high-vibration or impact-prone environments, conduct periodic tension checks and
inspections to verify long-term reliability and prevent stress-related wear.
Buying Cross Connectors
Professionals across Europe rely on Buisklem for high-quality cross connectors, designed for rigid and
load-bearing pipe assemblies. Available in various sizes, fastening types, and finishes, each connector
provides secure reinforcement for modular frameworks, steel constructions, and industrial pipe
structures. The precision-engineered clamping mechanism ensures a tight and stable fit, preventing
misalignment and structural shifting in heavy-duty applications.
With a large stock availability and fast order processing, Buisklem guarantees a reliable supply for
urgent projects and large-scale installations. Custom options, including special coatings, corrosion-
resistant materials, and reinforced designs, are available for specialist applications. A trusted European
logistics network ensures that professionals always have access to essential fastening solutions, ready
for immediate installation.